Large-volume subcutaneous injections
Transforming healthcare with large-volume subcutaneous solutions for patient-centered treatments
Biologics are revolutionizing the treatment landscape for many serious diseases, including cancer, metabolic disorders, cardiovascular conditions, genetic disorders, and immunological diseases. With over 6,200 drugs in development, 80% of which are biologics, the future of healthcare is set for significant advancements (source: Globaldata, May 2024). However, the administration of these complex medications presents unique challenges.
Traditionally, biologics have been administered via intravenous (IV) or subcutaneous (SC) routes in a hospital or doctor’s office. IV administration quickly achieves therapeutic levels in the bloodstream but is associated with high healthcare costs, time-consuming procedures, and the need for trained medical professionals. This creates a substantial burden on patients and healthcare systems, particularly for long-term and frequent treatments. With an aging population and an increase in chronic conditions, the financial impact on healthcare resources becomes even more significant.
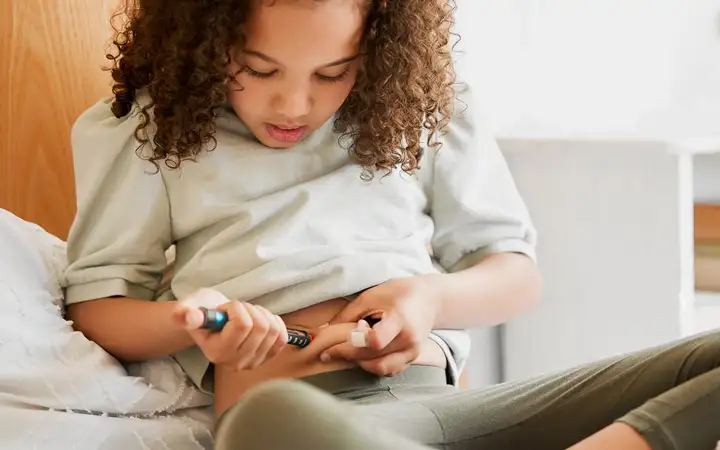
Subcutaneous injections offer a more patient-friendly alternative. Devices such as pens, autoinjectors, on-body devices, and infusion systems empower patients to self-administer medications for chronic conditions such as diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis at home. This approach improves patient adherence and reduces the overall treatment burden on caregivers and healthcare systems.
Are you ready for subcutaneous injections of large-volume biologics?
As technology evolves, the potential for self-administration increases, enhancing patient experience and adherence. However, subcutaneous delivery using pens, autoinjectors, on-body delivery systems, or infusion pumps faces challenges, particularly with high-viscosity or large-volume biologics, which must be addressed to fully benefit from SC administration.
Meeting tight timelines
Navigating new challenges
Ensuring patient-centered quality
Innovative primary packaging solutions for large-volume biologics
To address high-viscosity biologics and drug-container challenges, developers should use high-quality containers with low extractables and leachables (E&L) profiles. These containers are typically made from premium borosilicate glass or advanced polymers such as Cyclic Olefin Copolymer (COC) and feature modified silicone and specialized elastomers.Innovative containment and delivery systems such as autoinjectors are essential for managing the increased force needed for high-viscosity injections. Durable primary containers such as polymer syringes, glass syringes, and cartridges minimize damage from these forces. Alternatively, on-body delivery systems (OBDS) and infusion pumps can slowly infuse larger volumes of high-viscosity biologics.
At SCHOTT Pharma, we prioritize patient convenience and safety with solutions that ensure precise and user-friendly drug administration. Our cartridges and syringes feature precise geometry to provide accurate dosing and reduce injection forces. This enables seamless integration with a variety of injection devices, including pen injectors, autoinjectors, on-body delivery systems, and infusion pumps. By partnering with leading device suppliers, we guarantee a smooth container-device interface for reliable second sourcing. Our comprehensive regulatory and analytical support ensures a smooth path to market for your drug product.
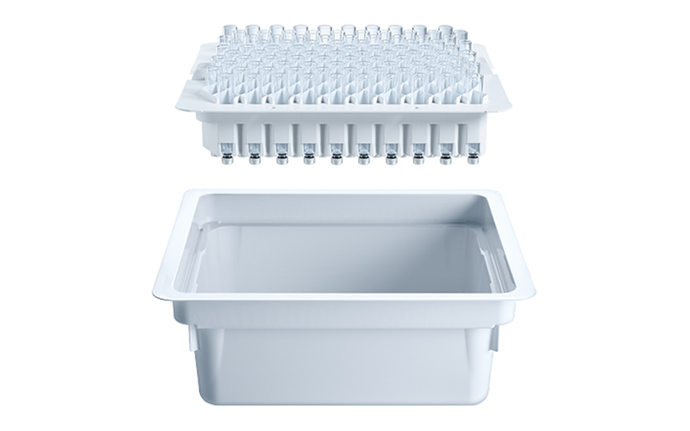
Biologics filling operations with ready-to-use containers
The limited patient population for biologics impacts filling operations, affecting the primary packaging in autoinjectors, wearable devices, and infusion pumps. As biologics are typically produced in smaller batches, pharmaceutical manufacturers have focused on cost-effective filling solutions. This has led to a trend in ready-to-use (RTU) containers using a standardized nest and tub format, facilitating the efficient use of filling lines and minimizing changeover time to meet evolving market demands. Additionally, RTU packaging arrives sterile at the manufacturing line, enabling fully aseptic manufacturing processes. SCHOTT Pharma has a wide network of fill-and-finish equipment manufacturers and CDMOs to enable fast filling of your drug.